Interest rates are vital economic factors that shape financial markets and determine the future of economies worldwide. In recent years, we have seen significant increases in interest rates, after a prolonged period of historic lows. While this shift has far-reaching implications, one key area of the global economy that stands to be impacted is Foreign Direct Investment (FDI).
In this article, we will explore the intricate ties between surging interest rates and FDI, providing insights into the role and factors affecting interest rates and their impact on foreign investment attraction.
Understanding Interest Rates
Interest rates are the cost of borrowing money and the return on investment for lenders. They are typically determined by central banks, like the Federal Reserve in the United States, through their monetary policy tools.
Central banks adjust interest rates primarily to control inflation and stimulate or cool down economic activity. When central banks lower interest rates, borrowing becomes cheaper, encouraging spending and investment, which can boost economic growth. Conversely, when rates are raised, borrowing becomes more expensive, discouraging excessive spending and helping to curb inflation. In essence, interest rates serve as a tool to manage the overall health of an economy.
Factors That Influence Rises in Interest Rates
As central banks carefully monitor and adjust interest rates to achieve specific economic objectives, several factors can trigger increases in interest rates:
Inflation Concerns:
Rises in interest rates counter inflation by making borrowing costlier, thereby reducing spending, as inflation decreases a country’s currency purchasing power. Central banks closely monitor inflation levels as they are crucial to determining rate increases.
Strong Economic Growth:
Central banks may boost interest rates to maintain economic stability when there is vigorous growth with lower unemployment. They increase rates to mitigate an overblown economy to prevent rising prices and asset bubbles.
Fiscal Policy:
Excessive government borrowing due to spending surpassing revenues can push up interest rates, especially when investors worry about the government’s ability to repay its debt. Increased borrowing raises demand for loans, causing lenders to seek higher returns, driving up rates.
Global Factors:
International economic conditions, such as changes in exchange rates can also influence rises in interest rates. For example, if a country’s currency is weakening relative to other currencies, it can make imports more expensive, potentially contributing to inflation. Central banks may raise interest rates to counteract this effect. Furthermore, the economic conditions in major trading partners and globally interconnected financial markets can spill over into a country’s economy. Economic downturns or crises abroad can lead to lower demand for a country’s exports, affecting its economic growth and potentially influencing its interest rate decisions.
The Current State of Interest Rates
Interest rates in the United States have been at historically high levels due to the persistently high levels of inflation over the past two years. Inflation has reached the highest annual rates since the early 1990s, and the effects of this are being felt throughout the economy.
To curb inflation, the Federal Reserve has increased interest rates to the highest level in 22 years. They are hoping that by raising interest rates borrowing and investing will become more expensive, thus reducing the demand for goods, services and labor.
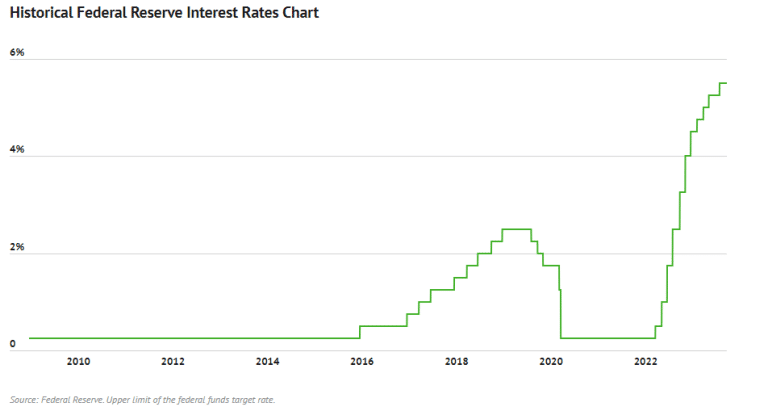
(Graph 1: Historical Federal Reserve Interest Rates Chart)
The federal reserve has been continuously monitoring the inflation rate, and despite 12 consecutive months of declines in consumer prices, in June, the inflation rate still showed a 3% increase year over year. While this has been the lowest annual inflation rate over the past two years, it is still significantly higher than the target rate of 2%.
Due to these persistent levels of inflation, the Federal Reserve last increased interest rates by a quarter-point in July, going from 5.25% to 5.50%. This was the 11th interest hike in the last 12 meetings, bringing current interest rates to levels that have not been seen since the housing market crash in 2007.
How Rising Interest Rates Affect FDI
Interest rates play a significant role in shaping the flow of Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) into a country’s economy as the level of interest rates in a host country can influence foreign investors’ decisions in several ways.
At its core, the rise in interest rates represents a cost increase for borrowed capital. This means that any business looking to finance new ventures or expansion – including FDI projects – will now face a greater cost. In many cases, this could make the difference between a project being viable or not.
The direct knock-on effect of this for Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) could be twofold:
1. Discouragement of New FDI Projects
The planning of any FDI project involves a thorough assessment of financial feasibility, within which lies the cost of capital. If borrowing becomes more expensive due to elevated interest rates, the predicted return on investment (ROI) may decrease. Subsequently, these new FDI projects may not look as attractive or feasible as they did with lower borrowing costs.
For example, say a European company is considering opening a new facility in Asia. This leap would already involve multiple risks, such as navigating different regulatory and cultural landscapes. If the interest rates rise in their home country, the costs of borrowing funds for this new venture rise. This additional financial risk might be enough to discourage the FDI project.
2. Potential Deterrence of Existing FDI Expansion
The escalating cost of borrowing doesn’t just affect new projects. It can also impact existing FDI where companies plan to reinvest or finance further expansion using borrowed capital. With the rising cost of borrowing, these reinvestment or expansion plans might need to be put on hold, reducing the flow of FDI.
To illustrate, consider an American company already operating a branch in Brazil and planning an expansion. If the U.S. interest rates rise, it might halt its expansion plan, inhibiting the anticipated FDI flow into Brazil.
Thus, as a country’s interest rates rise, it could experience a decrease in FDI activity. However, it’s crucial to understand that many other factors come into play such as the overall political and economic stability of the country.
Forecasting Future FDI and Interest Rate Correlations
Predicting future trends of interest rates and their impact on FDI isn’t straightforward due to numerous influencing factors. Most economists anticipate a fall in interest rates in 2024. However, forecasts are varied, with some expecting a modest decline while others foresee a more dramatic drop.
Fundamentally, the direction of interest rates largely depends on how well inflation is contained towards the target rate of 2 percent. Thus, continued monitoring of inflation rates is crucial to predicting future interest rate movements and their impact on FDI.
Tips for Investors Navigating the Impact of Interest Rates on FDI
Finally, as an investor, it’s essential to be aware of how rising interest rates could impact your investments. Here are some tips to navigate these waters:
1. Stay Informed:
Keep an eye on interest rate trends and economic news that may signal changes. Understanding these signals can help you anticipate shifts in FDI.
2. Factor in Higher Financing Costs:
With higher interest rates, the cost of borrowing increases. It’s crucial to factor this into your investment plans and calculations.
3. Monitor Inflation:
With inflation directly impacting interest rates, keep a close watch on inflation trends as well.
4. Consider the Economic Health of FDI Destination Countries:
High interest rates may indicate monetary stability, but they may also signal an overheated economy. Analyze the overall economic health of a country before investing.
5. Leverage Expert Advice:
Working with experienced financial advisors can help navigate the intricacies of Foreign Direct Investment amid changing interest rates.
Undoubtedly, rising interest rates play a significant role in FDI. While the potential for better returns and perceived stability may be attractive, higher rates can deter FDI by increasing financing costs and leading to adverse economic effects. As investors, understanding and monitoring the interplay between interest rates and FDI is crucial to making informed investment decisions.
More from ResearchFDI:




